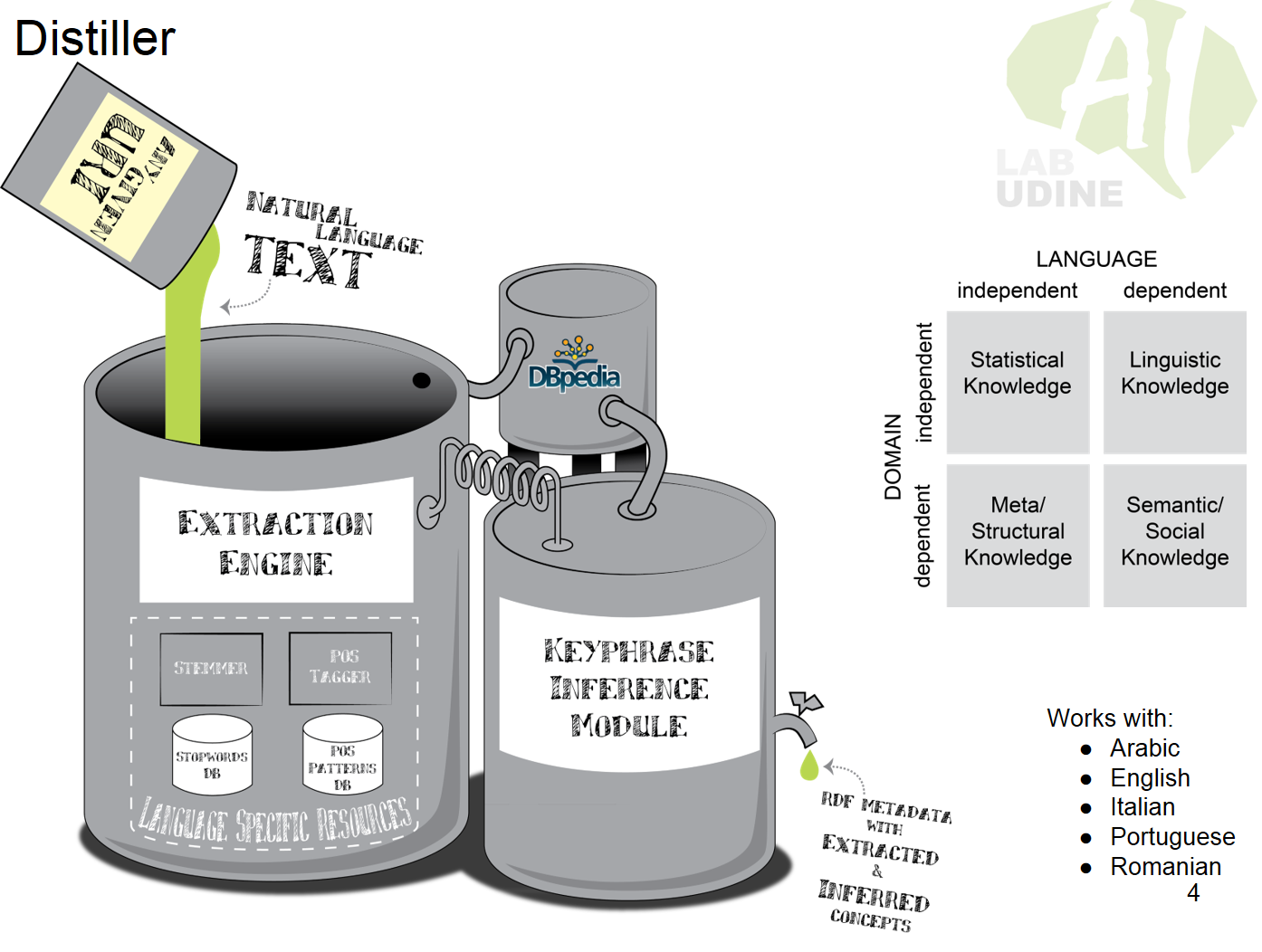
Arabic keyphrase extraction is a crucial task due to the significant and growing amount of Arabic text on the web generated by a huge population. It is becoming a challenge for the community of Arabic natural language processing because of the severe shortage of resources and published processing systems. In this paper we propose a deep learning based approach for Arabic keyphrase extraction that achieves better performance compared to the related competitive approaches. We also introduce the community with an annotated large-scale dataset of about 6000 scientific abstracts which can be used for training, validating and evaluating deep learning approaches for Arabic keyphrase extraction. Related publications: Helmy M., Vigneshram R. M., Serra G., Tasso C. Applying Deep Learning for Arabic Keyphrase Extraction. In: Proc. of the 4th International Conference on Arabic Computational Linguistics (ACLing 2018), November 17-19 2018, Dubai, United Arab Emirates. Resources: Arabic Abstracts Dataset