Generalized Born radii computation using linear models and neural networks
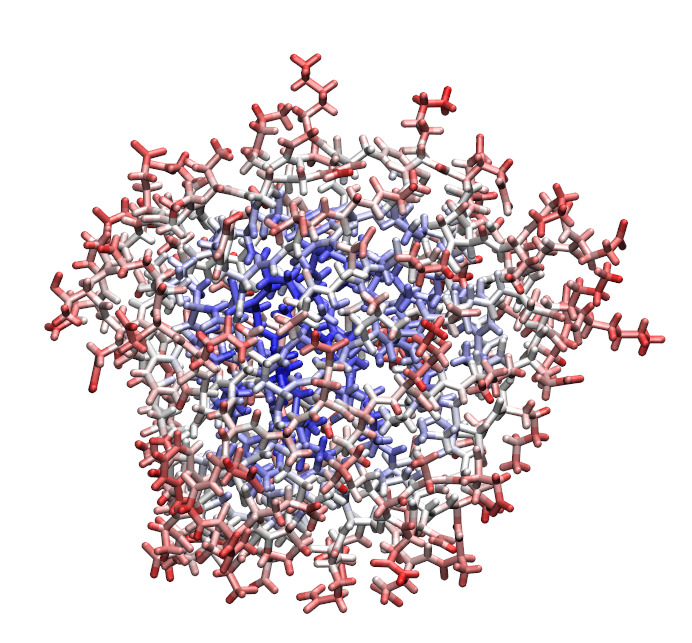
Implicit solvent models play an important role in describing the thermodynamics and the dynamics of biomolecular systems. Key to an efficient use of these models is the computation of Generalized Born (GB) radii, which is accomplished by algorithms based on the electrostatics of inhomogeneous dielectric media. The speed and accuracy of such computations is still an issue especially for their intensive use in classical molecular dynamics. Here, we propose an alternative approach that encodes the physics of the phenomena and the chemical structure of the molecules in model parameters which are learned from examples. In our project, GB radii have been computed using i) a linear model and ii) a neural network. The input is the element, the histogram of counts of neighbouring atoms, divided by atom element, within 16 Å. Linear models are ca. 8 times faster than the most widely used reference method and the accuracy is higher with correlation coefficient with the inverse of “perfect” GB radii […]
Fake News Detection (AILAB-Udine – MIT Boston)
In the last few years, we have assisted at the explosion of news sharing and commenting in social networks. While this practice has positive aspects, as it stimulates the debate, it has been polluted by the diffusion of unreliable news, generally referred to as Fake News. Since these contents are often produced with malicious intents and they have a tremendous real-world political and social impact, the Natural Language Processing (NLP) community has been called to propose algorithms for their identification. Most of the currently existing works are so far based on stylistic and linguistic peculiarity of the Fake News texts (such as excessive use emphasis and hyperbolic expressions). As time passes, however, the Fake News tend to be stylistically and linguistically more similar to Real News, so that Fact Checking remains as the only reliable approach to isolate them. In this project, we employ Artificial Intelligence to assess the reliability of news on the base of not only intrinsic criteria […]
We welcome Saida

Saida has joined us at the AILAB in the last days. She is a PhD student from Egypt. Her interests are in Machine Learning and Deep Learning, and in Fuzzy Logic too. We wish Saida to have a good time in our group and to achieve great goals in her work.
A new member joins AILAB

We are very pleased to welcome a new member of the AILAB. Giuseppe Lancioni joined us as a Ph.D. student whose main research focus will cover the Data Analysis and Natural Language Processing fields. Everyone in the AILAB team is looking forward to work with him and see him achieve great goals!